Fresh Or Canned Vegetables For A Renal Diet
If you live in an area where fresh vegetables are not readily available or affordable, you may feel your options are limited to canned vegetables. It may also be the case that fresh vegetables are not available at this time of year for you to choose.
If this is the situation that you are facing, you must consider many factors when choosing these items and you will need a renal diet grocery list.
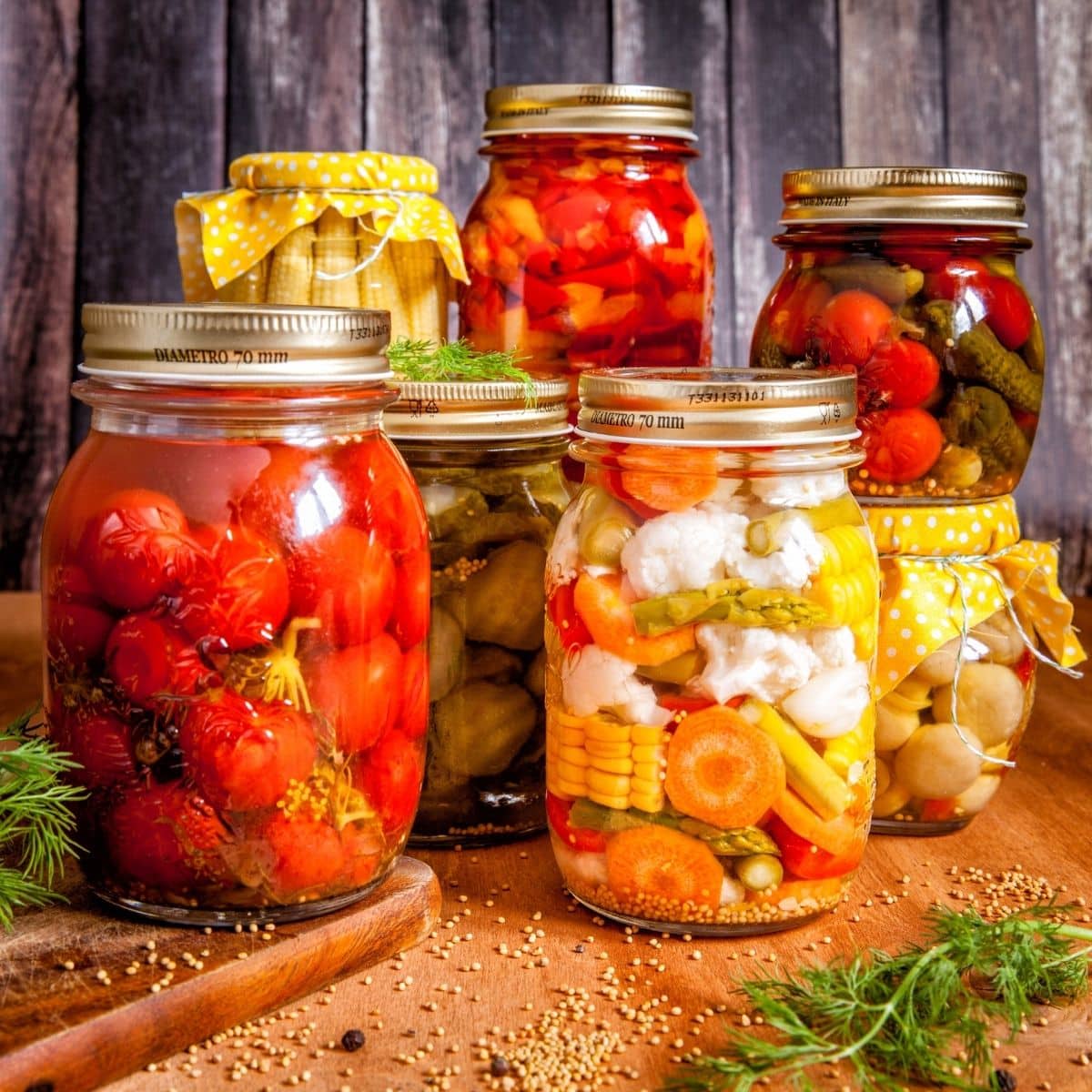

For people with kidney disease, you must take care to limit your consumption of protein, sodium, potassium, and phosphorus depending on your diet changes by stage of chronic kidney disease.
You may need to watch your carbohydrate intake if you have diabetes as well. Unfortunately, because of these factors, canned vegetables can be a little trickier to pick than fresh vegetables but you can find low sodium canned foods for CKD.
Don't forget you can choose frozen vegetables, and they are similar in nutritional content to what a fresh vegetable would be. So they may be a great compromise when you are really wanting to use fresh vegetables but they are not available.
And remember, even though they may cost a little more, you will be eating less meat or protein so your grocery bill should be in a better place!
Jump to:

Sodium
Generally, canned foods are high in sodium. Fortunately, these items also are required to list the sodium content on the nutrition label. This part of the label can be consulted to see if the item would be acceptable or not.
The percent daily value (%DV) that is on the food label should be no more than 6-10% to stay within the limits of your pre-dialysis renal diet. Most canned foods are significantly higher than this amount.
Look for items that are marked sodium free, very low sodium or low sodium. Items are marked as reduced sodium or light in sodium may be reduced to an acceptable level . Sometimes these canned foods still have a sodium level that is too high for your intake.
Another tip - you can rinse canned vegetables and reduce the sodium content by an average of 35%. It's a great way to use regular canned vegetables if you already have them in the house and don't want to discard them.
You can also check out these low sodium potluck dishes that go alongside the vegetables you choose to eat.
For More Recipes and Ideas --->> Get Your Free Meals and Recipes That Are Perfect for Pre-Dialysis Diets, Pre-Dialysis with Diabetes, or Dialysis Diets.
Potassium
Sometimes if there is no salt added, there may be added potassium content (low potassium diet menu) leading to increased potassium intake. You can notice if this is the case by checking the ingredient list. One form of potassium that is often used as a salt substitute is potassium chloride.
If this is added, usually the food is too high in potassium to consume. When reading the label, check for the word potassium in the ingredient listing - if it's at the top, you probably have too much.
Potassium is now required to be marked on nutrition labels, and manufactures add it for food products. If a food is under 200mg the RDA may label it as 6%. This is what is acceptable for you intake.
If it is 100mg or 3% the RDA, this is a low potassium food. If the item is above 6% it is too high for your current intake.
If potassium is not listed, you still need to be careful. You must be aware of vegetables that are low in potassium, and those that are potassium rich vegetables.
If you are not sure, it is better to make note of the vegetable and check before you risk it being high in potassium and affecting your low potassium diet for chronic kidney disease.
Phosphorus
Should you have phosphorus in your body when you're dealing with CKD? Labels are not required to post the phosphorus in foods. If it is posted as an RDI (recommended dietary intake) make sure it is under 15%. If an item is 50mg (5%) or less it is a low phosphorus food.
More than 15% is considered a high phosphorus food and should be avoided if your levels are high, which your doctor or dietitian can help you determine based on labs.
Read the ingredients list to understand if there is added phosphorus. Ingredients with the word "phos" in them are added phosphorus during processing and are absorbed at a much higher rate in humans than normal or organic phosphorus.
Carbohydrates
Sometimes canned vegetables have added sugar. If you have diabetes, you should be particularly concerned with this value. One carbohydrate serving is considered 15g.
This information can be found in the "total carbohydrates" category on the food label. Total sugar that is in a food is grouped into this value, making it a more accurate number to look for if you have diabetes.
Fiber also is something that you should pay attention to on the nutrition facts label. The higher the fiber, the better it is for your blood glucose control.f A good source is considered 10% of the %DV and a high source is 20% of the %DV.
Serving Sizes
Be careful to note what the serving sizes are in food since often they are much smaller than you would assume for your daily intake of any foods.
If you are consuming double the serving size, it is important to note that you are consuming double the sodium, potassium, phosphorus and carbohydrate amounts and thus they can be above your renal diet restrictions. The serving size is listed in the nutrition facts label.
It is rare that canned foods are better than fresh foods. There is much more to consider regarding canned vegetables. You still must be aware of which vegetables are high versus low in potassium and phosphorus.
Yet, it is possible to include these items in your diet by taking note of certain items that may be added such as sodium or potassium.
You can choose fresh and frozen vegetables, which will be lower in sodium, but you still need to pay attention to the potassium and phosphorus amounts in them because they could be a product that is high in potassium or phosphorus naturally.
Health Risks
For kidney patients, high levels of sodium, potassium, and phosphorus in the blood can be dangerous and can lead to various health complications.
Excess sodium can cause fluid retention, which can lead to swelling in the legs, ankles, and feet. It can also increase blood pressure, which can put a strain on the heart and blood vessels. This can increase the risk of heart disease, stroke, and other cardiovascular problems.
High potassium levels, also known as hyperkalemia, can cause muscle weakness, irregular heartbeat, and even cardiac arrest. Kidney patients are at a higher risk of developing hyperkalemia because their kidneys may not be able to remove excess potassium from the blood.
High phosphorus intake can lead to bone disease, joint pain, and muscle weakness. It can also contribute to the development of cardiovascular disease, as high levels of phosphorus can cause calcification of the blood vessels.
To prevent these risks, kidney patients should follow their recommended dietary intakes of sodium, potassium, and phosphorus set by their dietitian or their healthcare provider. They should also work with their healthcare provider to monitor their blood levels and adjust their medications as needed.

Benefits Of Fresh Vegetables
Fresh vegetables can provide a variety of nutritional benefits such as vitamins and minerals. They also offer a wide range of options, from leafy greens to root vegetables (vegetables low in phosphorus and potassium).
For those on a renal diet, fresh vegetables are especially beneficial as they have a low sodium content. Eating these vegetables can help lower blood pressure and reduce the risk of other health complications. Plus, they can easily be incorporated into delicious and nutritious meals.
All in all, fresh vegetables are an excellent choice for those looking to improve their diet and overall health.
Nutritional Benefits
Fresh vegetables such as cauliflower, cabbage, and bell peppers provide essential vitamins and minerals that help to keep the body functioning properly. Wondering if corn is good for CKD patients? It can be as a fresh food.
Plus, they are low in sodium and potassium as they are free from added salt, which means they won't put added strain on your kidneys.
Cooking methods like steaming and boiling help retain more nutrients than canned alternatives, which means nutrient absorption will be higher when consuming these veggies. You can add grilled foods for CKD to make healthy choices as well.
And don't forget about seasoning options such as herbs and spices like garlic powder or Italian seasoning; these add bold flavors without adding any extra sodium.
Plus, by varying the types of vegetables used in each recipe you’ll get more nutrition from your meal while also avoiding boredom from eating the same dishes day after day.
It's important to practice food safety for people with kidney disease whenever preparing meals involving fresh vegetables – especially when dealing with produce purchased at farmer’s markets or local grocers.
Make sure to thoroughly wash all fruits and veggies before consuming them (even if you plan on peeling them) so that harmful bacteria won't ruin your healthful efforts!
With such a wide variety of recipes available, it's never been easier or tastier to make sure you're getting enough nutrients while still following a renal diet.
Low Sodium Content
Fresh vegetables often contain less sodium than canned varieties, making them the ideal choice for lower sodium recipes. Eating low-sodium foods helps regulate blood pressure, which can be especially beneficial for those with kidney disease.
Looking at the leafy vegetables for salads and green vegetables for your plate can be a healthy way to get more fiber and vitamins with a lower source of phosphorus.
On the other hand, high levels of sodium in canned vegetables can lead to health risks such as high blood pressure and heart disease.
But even with fresh vegetables, there can be higher levels of sodium if you're not careful! That's why knowing which veggies have low-sodium content and practicing portion control will help ensure that your meals stay light on salt and full of flavor.
When considering fresh vegetable options, look no further than bell peppers, broccoli on a renal diet, cabbage, cauliflower, and onions. These colorful choices pack in plenty of vitamins and minerals while having very little sodium per serving.
Not only that, but these veggies are packed with antioxidants, so you're getting all the nutrition without the added salt.
With so many ways to enjoy them, there’s no excuse not to reap the rewards of their nutritional power.
Benefits Of Canned Vegetables
Is there sodium in fresh tomatoes? As long as you make sure that they are not high in sodium or potassium, canned vegetables can provide just as many nutrients as fresh vegetables and can be suited for a renal diet.
Plus, they're incredibly convenient; you don't have to worry about preparing or cooking fresh veggies and they're easy to store.
Cost-wise, canned veggies can be a great option since they're usually cheaper than fresh veggies and they don't spoil as quickly.
Convenience
When it comes to convenience, canned veggies have a lot going for them. Not only are they packaged in easy-to-store containers that require minimal space but also come with organic options with no added preservatives or sodium content.
We all know how hard it can be to find the time to shop for, prepare and cook fresh vegetables in a renal diet. Canned vegetables offer great convenience as they are pre-cooked and ready to eat or easily thrown into your favorite recipes.
When selecting canned vegetables, look at the label for preparation methods and storage tips. It’s important to rinse some varieties before use like black beans, kidney beans, or corn which will help reduce the amount of sodium content found in them.
It is essential to check the expiration date on cans prior to purchasing them for optimal safety during meal planning for kidney disease patients.
Canned vegetables provide an effortless way to add more fruits and veggies into our diets without having any extra hassle associated with preparing food from scratch every day--making sure you get sufficient nutrition while adhering to a renal diet has never been easier!
Cost
Cost is certainly a factor to consider when it comes to canned vegetables. Generally, organic varieties are more expensive than conventional ones due to the higher quality of ingredients and production methods used.
However, if you buy pre-chopped versions they may cost more than whole or cut pieces since they have already been minimally processed for convenience foods.
Buying in bulk can reduce your overall costs as well as make sure that you always have some on hand when needed.
Shelf life also plays an important role because cans are designed to last longer than their fresh counterparts; this means less frequent trips to the store which could save time and money over time and give you healthy foods as an option for daily meals with kidney failure.
Taking a grocery list for ckd patients to the store isn't a bad idea either, it will help you save a ton of money.
Lastly, storage considerations should be taken into account too; proper storage of food items will ensure that you don't lose out on any potential savings from expiration dates passing by unnoticed.
Vitamins And Minerals In Vegetables
Vegetables are an excellent source of vitamins and minerals, which are essential nutrients that our bodies need to function properly.
Different vegetables contain different types and amounts of vitamins and minerals, making it important to eat a variety of vegetables to ensure that we get all the nutrients we need.
Some of the most common vitamins found in vegetables include vitamin A, vitamin C, and vitamin K. In addition to vitamins, vegetables are also a good source of minerals such as magnesium and calcium.
Eating a variety of vegetables can help ensure that we get all the nutrients we need to support our bodies' functions.
Vitamin A
Vitamin A is an essential nutrient that plays a crucial role in maintaining healthy vision, skin, and immune function. It is a fat-soluble vitamin that is stored in the liver and can be found in a lot of foods, including vegetables.
Some of the benefits of vitamin A include:
- Vision health: Vitamin A is important for maintaining healthy vision, particularly in low light conditions. It helps to form the pigments that are necessary for the retina to detect light.
- Skin health: Vitamin A is important for maintaining healthy skin, as it helps to regulate the production of skin cells and sebum, which is the oil that keeps skin moisturized.
- Immune function: Vitamin A is important for maintaining a healthy immune system, as it helps to regulate the production and function of white blood cells.
Some vegetables that are good sources of vitamin A include:
- Carrots: Carrots are one of the best sources of vitamin A, as they contain high levels of beta-carotene, which is converted to vitamin A in the body. 1 cup of carrots (155 g) contains 142% of the DV.
- Lettuce: Lettuce is a good source of vitamin A, as well as other important nutrients such as vitamin C and fiber. 1 cup of lettuce (47 g) contains 23% of the DV.
- Sweet red pepper: Sweet red peppers are another great source of vitamin A. 1 large sweet red pepper (164 g) contains 29% of the DV.
Overall, incorporating vegetables that are high in vitamin A into your diet can help to support healthy vision, skin, and immune function. If you are worried you can't get all of this into your diet, then a ckd meal delivery may be for you!
Vitamin C
Vitamin C is a water-soluble vitamin that has many benefits for our health. It is an antioxidant that helps protect cells from damage, and is important for the production of collagen, which is a protein that helps to keep skin, bones, and blood vessels healthy.
Vitamin C is also important for immune function, as it helps to stimulate the production of white blood cells and keep them at a healthy level.
Eating habits play an important role when it comes to getting enough of this nutrient, as many food sources naturally contain Vitamin C. It's also easy to add more of it into your diet by incorporating some of these vegetables, which are good sources of vitamin C:
- Broccoli: Broccoli is an excellent source of vitamin C, as 1 cup provides 90.2% of the DV (broccoli and kidney disease).
- Brussels sprouts: 1 cup of brussels sprouts provides 79.8% of the DV.
- Cauliflower: 1 cup of cauliflower provides 57.3% of the DV (cauliflower renal diet).
As far as cooking methods go, lightly steaming or roasting are both excellent ways to preserve their nutritional value while adding flavor to your dishes.
With some mindful preparation and planning ahead anyone can make sure they get all the nutrients they need from either fresh or canned veggies!
Minerals
Now that we've discussed Vitamins C and A in vegetables, let's turn our focus to minerals. Vegetables are a good source of essential minerals, which are important for overall health and well-being.
Here are some examples of minerals found in vegetables and their benefits for kidney patients:
- Iron: Iron is important for the proper production of red blood cells. Some vegetables that are high in iron include broccoli, brussels sprouts, and green beans.
- Magnesium: Magnesium is important for bone health and blood pressure regulation. Some vegetables that are high in magnesium include cabbage, cauliflower, and green beans.
- Calcium: Calcium is important for bone health and helps to support proper muscle and nerve function. Some vegetables that are high in calcium include broccoli and kale.
It’s crucial to eat a variety of different vegetables, as too much of one vegetable can cause an overload of minerals that you don't want like potassium and phosphorus.
Consulting a healthcare professional or registered dietitian will help determine the best dietary choices for each patient’s needs.
Your potassium intake should be monitored if you have elevated levels of potassium in your blood.
Fiber Content Of Vegetables
Vegetables are an excellent source of dietary fiber, which is a type of carbohydrate that the body cannot digest.
For kidney patients, fiber is important for maintaining digestive health and preventing constipation, which can be a common problem for individuals with kidney disease.
Fiber can help to lower cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of heart disease, which is important for individuals with kidney disease who are at an increased risk of cardiovascular complications.
Some examples of high-fiber vegetables and their fiber content include broccoli (5 grams per cup), Brussels sprouts (4 grams per cup), cauliflower (2 grams per cup), and carrots (1.5 grams per medium carrot).
FAQs for Canned vs Fresh Vegetables
When considering what fresh or canned vegetables to include in a renal diet, it's important to pay attention to the amounts of salt and potassium in them.
It’s best to avoid certain vegetables like spinach, potatoes and tomatoes as they are high in potassium while sweet potatoes, carrots and squash may be consumed in moderation due to their lower potassium levels.
If you do consider eating potatoes, make sure you know about the amount of potassium in potatoes.
Ultimately, choosing the right combination of fresh and canned vegetables can help ensure proper nutrition during your renal diet.
In terms of a renal diet, there is no significant difference between frozen and canned vegetables. Both options can be a healthy addition to a renal diet, as long as they are low in sodium and potassium.
However, it is important to read the food labels carefully, as some canned vegetables may contain extra salt or other preservatives that can be harmful to individuals with kidney disease (reading nutrition facts labels with CKD).
Additionally, fresh vegetables may be a better option as they can be less expensive when they are in season.
Ultimately, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian to determine the best dietary choices for an individual with kidney disease.
A renal diet is a diet that is designed to help manage kidney disease by reducing the amount of certain nutrients that can be harmful to the kidneys. When it comes to vegetables, there are several fresh or canned options that are good choices for a renal diet.
Cauliflower, cabbage, bell peppers, green beans, onions, and radishes are all great fresh options that are low in potassium and are overall suitable for a kidney diet. Utilize these tips for a low potassium diet.
When it comes to canned vegetables, it is important to choose options that are low in sodium. Look for canned vegetables that are labeled as u0022no salt addedu0022 or u0022low sodium.u0022 Some good options include canned green beans, canned carrots, and canned tomatoes.
Draining or rinsing canned vegetables can also help to lower their salt content, making them healthier for renal patients. It is also very important to work with a healthcare provider or registered dietitian to develop a personalized renal diet plan.
It can be hard to know what not to eat on a renal diet. Fresh or canned vegetables should make up a significant part of your meal plan, as they provide important vitamins and minerals while being low in sodium content.
How often you include these foods will depend on individual needs, but having fresh options available several times per week is recommended for optimal health benefits.
When choosing vegetables for a renal diet, aim for plenty of color and variety-this way you'll get the most out of each vegetable's nutrition!
Enjoy Fresh And Canned Vegetables With Your Renal Diet
It's clear that fresh or canned vegetables can be a great addition to a renal diet. But as with all things, moderation is key. Don't go overboard and eat too many veggies at once - it could give you an upset stomach!
And don't forget about the frozen options either; they're just as tasty and can make for some delicious meals.
So if you have kidney disease, make sure to include some of these nutritious plants in your meals regularly – even if it’s only a few times a week. Trust me, your body will thank you for it!

















Thank you for this healthy Renal Diet information. I really do need a reminder of what I need to eat for my good health. Especially since I received my 2nd transplant.