How Can I Control My Kidney Disease Naturally
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) is a serious matter that not only affects your overall health, but also your life expectancy. Patients that have chronic kidney disease, more specifically those who make it to end stage renal disease, or kidney failure, are a lot more likely to suffer heart attacks. In fact, approximately one in four end stage renal disease patients dies of a heart disease.
Luckily, you can control your renal disease. There may be nothing you can do to regain kidney function that is already lost, but there is a lot you can do to slow or potentially even stop the progression of renal disease.
Start with dietary control, healthy lifestyle habits, and a positive attitude. With the right approach, you can manage your kidney disease and live a healthier life.
Jump to:
- Key Takeaways
- Understanding Chronic Kidney Disease
- Dietary Control and Self-Discipline
- Compliance With Medical Recommendations
- Healthy Lifestyle
- Positive Attitude and Mindset
- Tips for Making a Renal Diet Easier to Follow
- Hydration Considerations
- What to Do if You Have Kidney Disease
- Frequently Asked Questions
- You Can Control Your Kidney Disease
Key Takeaways
- Self-monitoring of symptoms and lifestyle adjustments are essential for managing kidney disease naturally.
- Following a healthy diet low in salt and fat, and high in fiber and plant-based proteins can help control kidney disease.
- Discipline and adherence to dietary restrictions and lifestyle changes are necessary for managing kidney disease naturally.
- Emotional support, stress management techniques, and a positive mindset contribute to successful kidney disease management.
Understanding Chronic Kidney Disease
Understanding Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) is the first step towards gaining control over its progression. CKD, a condition where the kidneys gradually lose function, demands knowledge and proactive measures.
In this section, we'll explore the critical aspects of CKD, from its causes and stages to symptoms and diagnosis. Armed with this knowledge, you'll be better prepared to take action, make informed decisions, and work towards managing and potentially slowing down the progression of this challenging condition.
For More Recipes and Ideas --->> Get Your Free Meals and Recipes That Are Perfect for Pre-Dialysis Diets, Pre-Dialysis with Diabetes, or Dialysis Diets.
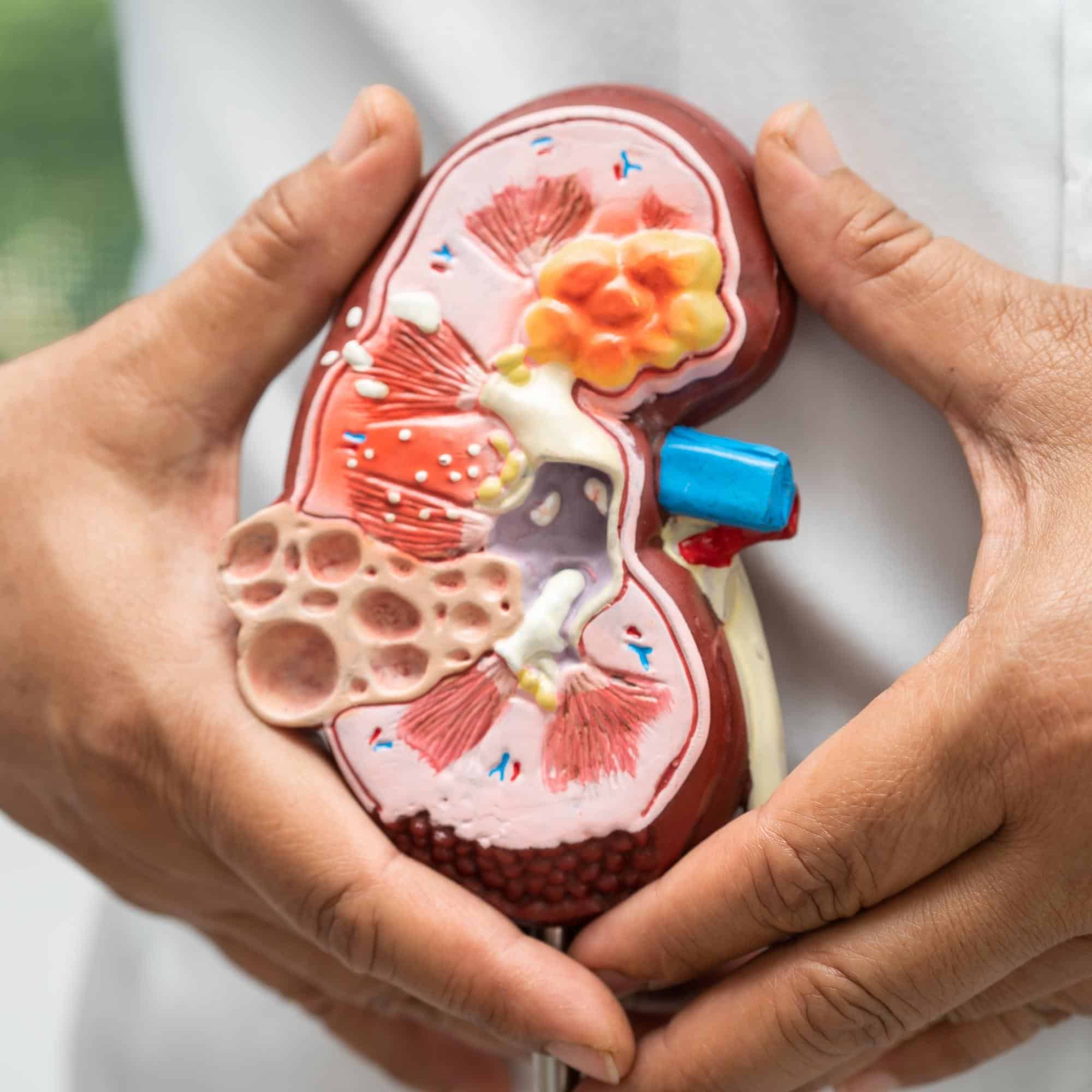
Renal Disease
Renal Disease or Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) is a long-term condition characterized by the gradual loss of kidney function over time. It's defined as kidney damage or decreased kidney function lasting for three months or more. CKD can be caused by various factors, with diabetes and high blood pressure being the leading culprits. Other causes include kidney infections, genetic disorders like polycystic kidney disease, and autoimmune diseases.
Diagnosis typically involves a combination of blood tests to measure blood creatinine levels and estimate Glomerular Filtration Rate (eGFR), as well as urine tests to check for protein or blood. Medical imaging and kidney biopsies may be used in specific cases. Early diagnosis and monitoring are crucial in managing CKD and preventing further kidney damage, as symptoms often don't appear until the disease is in advanced stages.
Stages of CKD
Chronic Kidney Disease is categorized into five stages based on the Glomerular Filtration Rate, which measures how effectively the kidneys filter waste from the blood.
- Stage 1 (GFR >90): Kidney damage is present, but GFR is normal. Symptoms are often absent.
- Stage 2 (GFR 60-89): Mild reduction in kidney function, with possible mild symptoms like fatigue or changes in urination.
- Stage 3 (GFR 30-59): Moderate kidney function decline. Symptoms like swelling, increased blood pressure, and anemia may appear.
- Stage 4 (GFR 15-29): Severe reduction in kidney function. Symptoms intensify, and patients may need dietary restrictions and medications.
- Stage 5 (GFR <15): End-Stage Renal Disease (ESRD), where kidneys are unable to function adequately. Dialysis (hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis) or kidney transplantation becomes necessary for survival.
The progression through these stages can be gradual or accelerated, depending on the underlying cause, management, and individual health. Early detection, lifestyle modifications, and appropriate medical intervention can slow the progression and improve the quality of life for individuals with CKD.
Dietary Control and Self-Discipline
Dietary control plays a pivotal role in managing Chronic Kidney Disease and preventing its progression. This section delves into the essential dietary restrictions that individuals with CKD must adhere to. It underscores the importance of self-discipline when it comes to food choices and portion sizes.
By understanding these dietary restrictions and maintaining a sense of control, individuals with CKD can significantly enhance their overall well-being and slow down the advancement of this condition. It's a crucial aspect of self-care for those navigating the complexities of CKD management.
Dietary Restrictions
Dietary restrictions in Chronic Kidney Disease are essential for managing the condition and preventing further kidney damage. These restrictions often involve limiting the intake of protein, phosphorus, potassium, sodium, and sometimes fluid. This specialized diet is also known as the renal diet.
Here is a brief overview of the restrictions often prescribed in a kidney friendly diet.
- Protein: Reducing protein intake helps minimize the production of waste products that the kidneys would normally filter out. High-quality, low-protein sources like lean meat and fish are preferred.
- Phosphorus: Excessive phosphorus can lead to bone and heart problems in CKD. Foods rich in phosphorus, such as dairy products and some legumes, should be limited.
- Potassium: Elevated potassium levels can affect heart rhythm. Patients are advised to avoid high-potassium foods like bananas, oranges, and potatoes.
- Sodium: Sodium can cause fluid retention and high blood pressure. Reducing salt intake by avoiding processed and restaurant foods is crucial.
- Fluid: Some people with kidney disease may need to restrict fluid intake to avoid fluid overload and swelling.
Adhering to these dietary restrictions, while ensuring adequate nutrition, can help slow CKD progression and manage associated complications. However, it's important to work closely with a healthcare team or dietitian to create an individualized plan that suits the patient's specific needs and stage of CKD.
Dietary Control
Dietary control is of paramount importance in managing Chronic Kidney Disease. It plays a vital role in slowing the progression of the condition and reducing complications.
Foods to Avoid:
- High-Protein Foods: Reducing high-protein foods like red meat can alleviate the workload on the kidneys.
- High-Phosphorus Foods: Phosphorus-rich foods like dairy products and nuts should be limited to prevent bone and heart problems.
- High-Potassium Foods: Foods like bananas and potatoes, which are high in potassium, can disrupt heart rhythms and should be moderated.
- High-Sodium Foods: Limiting salt intake is crucial to avoid fluid retention and high blood pressure.
- Excessive Fluids: Some individuals may need to restrict fluid intake to prevent fluid overload.
Healthier Options:
- Low-Protein Alternatives: Opt for lean protein sources like chicken or fish.
- Phosphorus Control: Consume low-phosphorus foods like rice and pasta.
- Potassium Moderation: Choose low-potassium fruits and vegetables such as apples and green beans.
- Low-Sodium Choices: Use herbs and spices to flavor food instead of salt.
- Fluid Management: Follow recommended fluid limits and monitor intake.
Working with a registered dietitian is crucial to create a personalized dietary plan that meets individual needs and CKD stage. This control can help improve overall health and quality of life for those with CKD.
Self-Discipline
Self-discipline is a cornerstone of success in maintaining dietary restrictions within a renal diet for individuals with Chronic Kidney Disease. CKD demands strict adherence to dietary guidelines, as even minor lapses can exacerbate the condition and its complications.
Key Aspects of Self-Discipline:
- Portion Control: Controlling portion sizes is vital to manage nutrient intake, especially in terms of protein, phosphorus, and potassium.
- Mindful Eating: Developing mindfulness around food choices helps in making conscious decisions that align with dietary restrictions.
- Monitoring Labels: Reading food labels diligently to identify hidden sources of restricted nutrients is crucial.
- Staying Informed: Continuously educating oneself about CKD dietary recommendations empowers individuals to make informed choices.
- Seeking Support: Engaging with support groups, healthcare providers, and dietitians can provide the guidance and motivation needed to maintain discipline.
- Long-Term Commitment: Recognizing that CKD is a chronic condition necessitating lifelong dietary discipline is essential.
Self-discipline not only preserves kidney function but also minimizes the risk of complications like cardiovascular disease. It empowers individuals to actively participate in their health management, ultimately enhancing their quality of life.

Compliance With Medical Recommendations
Your physicians and healthcare providers are there to help you and walk you through this often difficult process. It is important to follow their instructions. Take your medications as directed, follow dietary recommendations, show up to your appointments, and do what needs to be done to stay as healthy as possible.
Remember also that your doctor is on your side. Whenever you have questions or concerns about your condition, medications, or other treatments, make sure you bring them up. You can learn a lot by simply asking questions and listening to the answers. Keep a journal and write down questions that you have for your doctor, then take it with you. It is easy to forget some questions when you are at the doctors office, this way you will have a list.
Medication Adherence
Medication adherence is paramount for individuals managing Chronic Kidney Disease to control symptoms, slow disease progression, and prevent complications. Maintaining a strict medication regimen can be challenging, but there are essential tips to help ensure adherence:
- Understand Medications: Knowledge is power. Understand why each medication is prescribed, its purpose, and potential side effects. This clarity fosters commitment.
- Set a Routine: Incorporate medications into your daily routine, associating them with other activities like meals or bedtime.
- Use Pill Organizers: These help organize multiple medications, reducing the chance of missed doses.
- Alarms and Reminders: Set alarms or smartphone reminders to prompt medication schedules.
- Keep a Medication Journal: Document doses, any side effects, and refill dates. It aids in tracking progress and ensures timely refills.
- Involve a Support System: Family members or caregivers can assist in reminding and organizing medications.
- Regular Check-Ins: Maintain open communication with your healthcare team. Discuss any challenges or concerns regarding medications.
- Refill Medications Promptly: Avoid running out of medications by refilling prescriptions well in advance.
- Pharmacy Consultations: Utilize pharmacists for medication reviews and clarifications.
- Travel Planning: Plan ahead for vacations or trips to ensure you have an adequate supply of medications.
- Medication Updates: Keep your healthcare provider informed about all medications, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements.
Adhering to medications is crucial in managing CKD, as missed doses or improper use can lead to disease exacerbation and complications. By incorporating these strategies and maintaining open communication with healthcare providers, CKD patients can better navigate their medication regimens and improve their overall health outcomes.
Scheduled Appointments
Regular follow-up appointments are crucial for CKD patients to effectively manage their condition. These appointments allow healthcare providers to monitor kidney function, adjust medications, and identify any complications early.
Missing scheduled appointments can lead to uncontrolled blood pressure, electrolyte imbalances, and other issues that can accelerate CKD progression. It's also an opportunity for patients to discuss concerns, ask questions, and receive guidance on lifestyle modifications and dietary changes.
Consistent follow-ups empower patients to take an active role in their healthcare, helping them make informed decisions to slow down CKD's progression and reduce the risk of complications like cardiovascular disease and kidney failure. Therefore, prioritizing and attending these appointments is essential for better kidney health and an improved quality of life for CKD patients.
Healthy Lifestyle
Doctors’ visits and medications can only do so much. You can make a huge difference in your own health outcomes by taking control of your overall lifestyle. Eating right, exercising daily at your own level of ability, and living an overall healthy lifestyle can make everything so much easier on you.
You would be surprised, for example, at just how much dietary changes can help your struggle with renal disease. You might also be surprised how delicious eating healthy can be, and how great you will feel after a nice long walk.
Physical Activity
Physical activity plays a pivotal role in the management of Chronic Kidney Disease. Regular exercise offers numerous benefits for CKD patients. Firstly, it can help manage common comorbidities like hypertension and diabetes, which are significant contributors to CKD.
Secondly, exercise improves cardiovascular health, reducing the risk of heart-related complications that often accompany CKD. Additionally, it helps control weight and maintain a healthy BMI, easing the strain on the kidneys.
Furthermore, physical activity can enhance muscle strength and endurance, which are essential for daily activities and overall well-being. Exercise also promotes better mental health, which is crucial for individuals dealing with the emotional impact of CKD.
However, exercise should be tailored to an individual's specific needs and fitness level, as excessive or inappropriate activities can be harmful. Consulting with a healthcare provider or a physical therapist to create a personalized exercise plan is highly recommended for CKD patients.
By incorporating regular physical activity into their routine, CKD patients can improve their overall health, slow down disease progression, and enhance their quality of life.
Self-discipline
Beyond diet and exercise, several other lifestyle changes are crucial for managing Chronic Kidney Disease. These include:
- Smoking Cessation: Quitting smoking is vital, as smoking can worsen kidney damage and increase the risk of cardiovascular issues.
- Alcohol Moderation: Limiting alcohol consumption is advisable, as excessive alcohol can strain the kidneys and interact negatively with medications.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress can exacerbate CKD symptoms. Techniques such as meditation, yoga, or counseling can help manage stress levels.
- Adequate Sleep: Getting enough quality sleep is essential for overall health and can aid in controlling blood pressure and reducing inflammation.
- Medication Adherence: Following prescribed medications diligently is crucial to manage underlying conditions contributing to CKD, such as hypertension or diabetes.
- Hydration: Maintaining proper hydration is important, but fluid intake should be monitored, especially if recommended to restrict fluids.
- Avoiding Over-the-Counter Medications: Non-prescription medications, like NSAIDs, should be avoided unless approved by a healthcare provider, as they can harm the kidneys.
- Regular Monitoring: Keeping up with routine check-ups and lab tests is essential to track kidney function and overall health.
These lifestyle changes, when combined with a renal-friendly diet and appropriate exercise, can significantly improve the well-being of CKD patients and help manage the condition effectively.
Positive Attitude and Mindset
No one can deny that being diagnosed and living with renal disease can be hard, but there is something to be said about a positive attitude. Going into your doctors appointments with a sense of purpose, finding a way to enjoy your new way of eating and living, and simply getting out to smell the flowers can have a big impact on your overall experience with renal disease.
Remember that you are in control of you, and that means that you have a level of control over your disease that is not insignificant. The overall attitude and action to do what needs to be done and live as healthily as possible can and will make a difference. You can make yourself a lot more comfortable, enjoy life, and extend your life as well.
Acknowledge Challenges
Acknowledging and addressing the challenges of living with Chronic Kidney Disease is an integral aspect of maintaining a positive attitude and effective disease management. Here's how:
Firstly, it's crucial to accept that CKD is a part of your life and to recognize your feelings and concerns. This acceptance is the first step towards proactive management. Education also plays a pivotal role. Learning about CKD, its stages, and its implications empowers you to make informed decisions about your health.
Furthermore, seeking emotional support is essential. Whether from friends, family, support groups, or mental health professionals, sharing your concerns can alleviate emotional burdens. Practicing self-compassion is another key component. Be kind to yourself, as CKD is a long-term condition with its ups and downs.
Setting achievable health goals, cultivating a positive mindset, and developing healthy coping mechanisms for stress are essential strategies. Regular communication with your healthcare team is also vital. By maintaining open communication, you can share concerns and questions, addressing issues promptly. Overall, acknowledging these challenges and taking proactive steps fosters resilience and empowers individuals to lead fulfilling lives despite CKD.
Appreciate Changes
Having a positive attitude and mindset can help you appreciate the changes in your life brought on by your kidney disease. It's important to recognize the emotional impact you may experience and focus on managing stress.
Making lifestyle changes and taking time for self-care can help you stay positive and focused on the changes that come with managing your kidney disease. It's important to make sure you're taking care of your mental health by engaging in activities and practices that help you stay positive.
While it can be difficult to adjust to lifestyle changes, it's important to remember that they can be beneficial for your overall health. Make sure to practice stress management techniques and focus on what you can do to make your life easier.
Appreciate the changes and use them as an opportunity to focus on your emotional and mental wellbeing.

Tips for Making a Renal Diet Easier to Follow
Making a renal diet easier to follow can be achieved by researching and planning meals. Preparing the meals ahead of time is also helpful. Taking the time to understand the diet and plan ahead can make it easier to stick to the diet and help manage kidney disease.
Research & Planning
Creating a renal diet plan is a complex but crucial aspect of managing Chronic Kidney Disease. Research and planning are of paramount importance in this process.
Firstly, research involves understanding the specific dietary restrictions and needs associated with CKD. This includes learning about foods that are high in phosphorus, potassium, sodium, and protein, as these can be detrimental to kidney function. Additionally, research helps in identifying foods that are kidney-friendly and provide essential nutrients without burdening the kidneys.
Planning is the practical application of this knowledge. It involves designing a well-balanced diet that adheres to the dietary restrictions while ensuring adequate nutrition. Planning also considers individual factors such as the CKD stage, other health conditions, and personal preferences. Moreover, planning ensures meal variety to prevent monotony and encourages compliance.
In essence, research and planning lay the foundation for a successful renal diet plan. They enable individuals with CKD to make informed food choices, manage their condition effectively, and maintain their overall health and well-being.
Meal Prep
By prepping your meals ahead of time, you can make sticking to a renal diet much easier. Meal planning can help reduce stress, save time, and ensure healthy kidney health.
| Meal Planning | Portion Control | Food Choices |
| Plan meals ahead of time | Control portion sizes | Choose foods that support kidney health |
| Schedule grocery trips | Monitor calorie intake | Avoid processed and high-sodium foods |
| Make a grocery list | Avoid over-eating | Incorporate more fruits and vegetables |
| Stick to the plan | Reduce salt intake | Limit high-potassium foods |
| Make use of leftovers | Monitor protein intake | Avoid sugary drinks and snacks |
Stress management and mindful eating are also key components of controlling kidney disease. When it comes to meal planning, being organized and proactive can help you make the best food choices for your health.
Hydration Considerations
Hydration is a critical aspect of managing Chronic Kidney Disease. Understanding which beverages to choose and how to navigate fluid restrictions, if necessary, is essential for kidney health. In this section, we'll delve into the importance of staying well-hydrated while balancing the restrictions that CKD may impose. Making informed choices about what you drink can significantly impact your kidney function and overall well-being throughout your CKD journey.
Healthy Beverages
Choosing the right beverages is vital for individuals managing Chronic Kidney Disease to support kidney health and maintain proper hydration. Healthy beverage options for CKD patients include:
- Water: The most kidney-friendly option, as it helps flush waste and toxins from the body.
- Herbal Tea: Caffeine-free herbal teas like chamomile, hibiscus, or ginger provide hydration without the drawbacks of caffeine.
- Lemonade or Limeade: These citrus-based drinks can add flavor without excessive potassium and phosphorus.
- Cranberry Juice (in moderation): It's lower in potassium and can be beneficial for urinary tract health, but should be consumed in moderation due to sugar content.
- Apple Juice: Low in potassium and a refreshing option for CKD patients.
Beverages to be avoided or limited for CKD patients include:
- Soda: High in phosphorus and often containing excessive sugars or artificial sweeteners.
- Sports Drinks: These are typically high in potassium and may contain excessive sugars.
- Energy Drinks: These can be loaded with caffeine, sugar, and other stimulants, which are not suitable for kidney health.
- Excessive Fruit Juices: Fruit juices can be high in natural sugars and potassium, so they should be consumed in moderation.
CKD patients should consult their healthcare team or dietitian to create a customized beverage plan that aligns with their specific dietary restrictions and needs, as individual requirements may vary.
Fluid Restrictions
Fluid restrictions are often a crucial aspect of managing Chronic Kidney Disease. In CKD, the kidneys' ability to excrete excess fluid may be impaired, leading to fluid buildup in the body (edema) and potentially causing complications like high blood pressure and heart issues.
The extent of fluid restriction varies depending on the individual's stage of CKD and their specific needs. Typically, healthcare providers or dietitians recommend daily fluid intake limits to prevent excessive fluid buildup. These limits can range from around 1,000 to 2,000 milliliters per day, but it's important to note that the restriction may change as the disease progresses.
Adhering to fluid restrictions is essential for maintaining kidney health and avoiding complications. Patients can monitor their fluid intake by measuring fluids consumed and limiting high-fluid foods like soups, ice cream, and watery fruits and vegetables. Staying hydrated while respecting these limits requires careful planning and close communication with a healthcare team to ensure the best possible outcomes in CKD management.
What to Do if You Have Kidney Disease
Preventing and managing Chronic Kidney Disease is a vital aspect of maintaining overall health. This section explores strategies to reduce the risk of CKD and effectively manage its progression.
From controlling underlying conditions like diabetes and hypertension to adopting a kidney-friendly lifestyle, we delve into the proactive measures individuals can take to safeguard their kidney health. Understanding the risk factors and embracing preventive actions can make a significant difference in averting the onset or progression of CKD, ensuring a healthier future.
Risk Factors
Effectively managing risk factors like diabetes and hypertension is paramount in preventing and controlling Chronic Kidney Disease. For individuals with diabetes, maintaining optimal blood sugar levels through medication, diet, and regular monitoring is crucial. Likewise, individuals with hypertension must keep their blood pressure in check, often requiring medication, dietary modifications, and lifestyle changes.
A kidney-friendly diet low in sodium and high in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can benefit both conditions. Additionally, regular exercise aids in weight management and overall health. It's imperative for those at risk or with these conditions to adhere to prescribed medications and attend regular check-ups to detect and address any issues promptly.
By diligently managing these risk factors, individuals can significantly reduce their likelihood of developing CKD and, if already diagnosed, slow its progression, ultimately preserving kidney function and improving their overall quality of life.
Prevention
Preventing Chronic Kidney Disease involves a proactive approach to maintaining kidney health. The first step is to manage chronic conditions effectively. Conditions like diabetes and hypertension significantly contribute to CKD risk. It's crucial to keep them under control through medication, lifestyle changes, and regular monitoring.
Diet plays a pivotal role in kidney health. Adopting a kidney-friendly diet is essential. This diet should be low in sodium, phosphorus, and potassium while being rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. It's important to limit processed and high-sugar foods to reduce the strain on your kidneys.
Staying hydrated is also important. While maintaining adequate fluid intake is crucial, it's equally important to follow any prescribed fluid restrictions if you have advanced CKD.
Regular exercise can help maintain a healthy weight and overall health, reducing the risk of conditions that can harm your kidneys. Avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption is equally vital.
Medication adherence is a must. Take prescribed medications as directed by your healthcare provider to manage chronic conditions effectively.
Monitoring kidney health through regular check-ups and kidney function tests, especially if you have risk factors, is essential. Managing stress with stress-reduction techniques can also contribute to overall kidney health.
Lastly, limiting the use of over-the-counter pain medications like nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) is advisable, as they can harm the kidneys with prolonged or excessive use. By embracing these preventive measures and maintaining a healthy lifestyle, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of developing CKD and enjoy better kidney health.
Frequently Asked Questions
While natural treatments may complement conventional care, they are not a substitute for medical treatment for kidney disease. It's essential to consult with a healthcare provider for a comprehensive treatment plan. Natural approaches may include dietary changes like reducing sodium and potassium intake, staying hydrated, and incorporating kidney-supportive foods. Herbal remedies, like astragalus and nettle leaf, are sometimes considered, but their safety and efficacy vary. Always discuss natural treatments with a healthcare professional to ensure they align with your medical treatment and don't pose any risks or interactions.
Regular physical activity can benefit overall health, including kidney health. Aerobic exercises like walking, swimming, and cycling can help improve cardiovascular health, which is closely linked to kidney function. Strength training exercises may enhance muscle mass, which can support metabolic and blood sugar control (what is metabolic syndrome?). Exercise also helps maintain a healthy weight and blood pressure, reducing the risk of kidney disease. However, it's crucial to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any exercise regimen, especially if you have existing kidney issues. They can offer guidance on suitable activities and intensity levels tailored to your individual health status.
Chronic kidney disease can lead to several long-term effects. These include an increased risk of cardiovascular disease, anemia, bone disease, and electrolyte imbalances. As CKD progresses, it can ultimately result in end-stage renal disease (ESRD), necessitating dialysis or a kidney transplant. Additionally, CKD can affect overall quality of life due to symptoms like fatigue, difficulty concentrating, and reduced kidney function. Managing CKD through medication, lifestyle changes, and regular check-ups can help mitigate these long-term effects and slow the progression of the disease, improving the overall outlook for individuals with CKD.
Preventing kidney disease involves managing risk factors. This includes maintaining a healthy blood pressure, controlling blood sugar if you have diabetes, adopting a balanced diet low in sodium and high in fruits and vegetables, staying hydrated, and avoiding excessive use of medications like NSAIDs. Regular check-ups are essential to monitor kidney function. Avoiding tobacco and limiting alcohol intake also play a role. Overall, a healthy lifestyle and early intervention for underlying conditions can significantly reduce the risk of developing kidney disease.
Medications can help manage kidney disease and its complications. For example, ACE inhibitors or ARBs may be prescribed to control blood pressure and protect kidney function. Phosphate binders and vitamin D supplements can manage mineral imbalances. Erythropoiesis-stimulating agents treat anemia, and diuretics help with fluid retention. Additionally, medications to control diabetes or reduce cholesterol levels may be necessary. The choice of medication depends on the underlying cause and stage of kidney disease, and it's essential to follow a healthcare provider's guidance to ensure safe and effective treatment.
You Can Control Your Kidney Disease
Living with kidney disease isn't easy, but with the right attitude and lifestyle changes, you can control it and lead a healthy life.
It's important to be compliant with your doctor's advice, eat a balanced renal diet, stay hydrated without overloading on fluids, and consider lifestyle changes.
There are many things your can do to control your renal disease, knowledge is important, so keeping up to date is important.